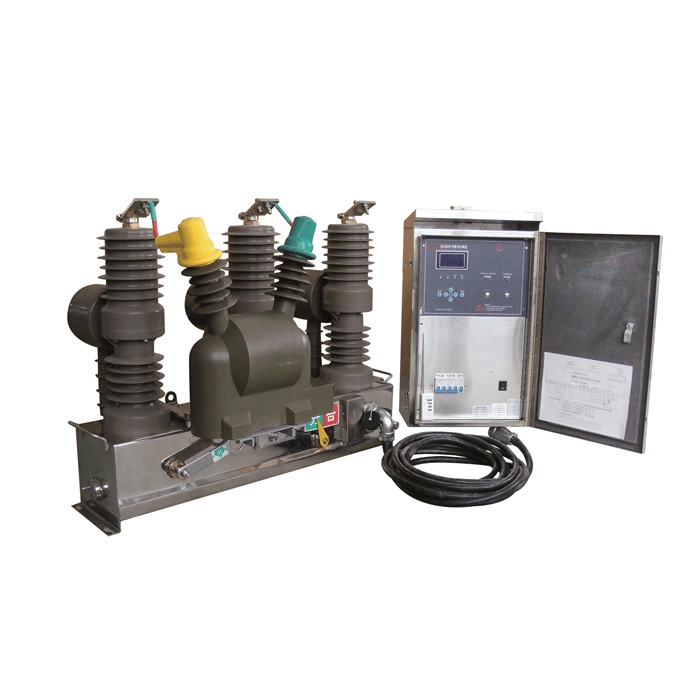
Transformer function
The function of the voltage transformer is to convert the high voltage into a standard secondary voltage of 100V or lower in proportion to the use of protection, metering and instrumentation devices. At the same time, the use of voltage transformers can isolate high voltages from electrical workers. Although the voltage transformer is also A device that works according to the principle of electromagnetic induction, but its electromagnetic structure relationship is opposite to that of a current transformer. The secondary circuit of the voltage transformer is a high-impedance circuit, and the magnitude of the secondary current is determined by the impedance of the circuit. When the secondary load impedance decreases, the secondary current increases so that the primary current automatically increases a component to satisfy the electromagnetic balance relationship between the primary and secondary sides. It can be said that the voltage transformer is a special transformer with limited structure and use form.
Voltage transformer is an indispensable electrical appliance in power transmission and power supply systems such as power plants and substations. Precision voltage transformer is an instrument used in electrical testing laboratory to expand the quantity limit and measure voltage, power and electric energy.
Voltage transformers are very similar to transformers and are used to transform the voltage on the line. However, the purpose of transformer voltage conversion is to transmit electrical energy, so the capacity is very large, and it is generally calculated in kVA or MVA; and the purpose of voltage transformer conversion is mainly for measuring instruments and relay protection devices. Power supply, used to measure the voltage, power and electric energy of the line, or used to protect the valuable equipment, motors and transformers in the line when the line fails, so the capacity of the voltage transformer is very small, generally only a few volt-ampere, dozens of Volt-ampere, the maximum does not exceed one thousand volt-ampere.
Why do you need to convert the voltage on the line? This is because the voltage on the line varies according to the different conditions of power generation, transmission and electricity consumption, and the difference is very different. Some are low-voltage 220V and 380V, and some are high-voltage tens of thousands of volts or even hundreds of thousands of volts. To directly measure these low-voltage and high-voltage voltages, it is necessary to make corresponding low-voltage and high-voltage voltmeters and other instruments and relays according to the size of the line voltage. This will not only bring great difficulties to the production of the instrument, but more importantly, it is necessary to directly make a high-voltage instrument and measure the voltage directly on the high-voltage line. That is impossible, and absolutely not allowed.
If a voltage transformer is connected to the line to convert the voltage, then the low-voltage and high-voltage voltages on the line can be uniformly converted into one or several low-voltage voltages according to the corresponding ratio, as long as one or several types of voltage specifications are used. And relays, such as general-purpose 100V meters, can measure and monitor the voltage on the line through voltage transformers.